Tooth decay or dental caries is one of the most common bacterial infections that affect the teeth. It is a major oral health problem in most industrialised countries, affecting 60–90% of schoolchildren and the vast majority of adults.
How is your tooth looks like?
Our teeth are the hardest substances in our body. Besides being used for chewing, the teeth play an important role in speech. Our teeth include the parts:

- Enamel: The hardest, white outer part of the tooth. Enamel is mostly made of calcium phosphate, a rock-hard mineral.
- Dentin: A layer underlying the enamel. Dentin is made of living cells, which secrete a hard mineral substance.
- Pulp: The softer, living inner structure of teeth. Blood vessels and nerves run through the pulp of the teeth.
- Cementum: A layer of connective tissue that binds the roots of the teeth firmly to the gums and jawbone.
- Periodontal ligament: Tissue that helps hold the teeth tightly against the jaw.
How do Decay (caries) form?
Our teeth are bathed in saliva with almost neutral PH, when there is an acidic environment around the teeth, a process called demineralization occur. Tooth demineralization refers to a process where an acidic environment leaches some of the mineral content (such as calcium) out of a tooth's calcified tissues (enamel and dentin).
Plaque is a white, sticky layer on the tooth structure which forms all the time. Without proper brushing, the plaque can become thicker. Plaque is a great "home" for bacteria. They are protected in their "home" from being washed away by saliva flow. If you fail to destroy their "home", they will start to build the "Great Roman Civilization".

They consume food and create waste products, just like we do. As it happens, the waste products they created are very acidic (they have a pH of 4 and lower) and cause tooth demineralization.
Role of Our Saliva
Our Saliva are "soldiers" in our mouth that help to neutralize the acidic solution produced by the bacteria. The minerals in the saliva would help to remineralized inital demineralization process. However, if the process of demineralization continues, the protective action of saliva will fail and cavities/ decay (caries) occurred.
Remember, you and your oral bacteria share the same menu.
Keep in mind that the things you eat are the same food items that are available to the bacteria that live in your mouth. So, when you consume foods that contain sugars, they get a meal too. And within minutes they start producing the acids that cause tooth decay. So brush your teeth properly from now on.
What Are The Stages Of Tooth Decay?
There are five key stages of tooth decay, and these are characterized by the tooth decay symptoms that are exhibited:
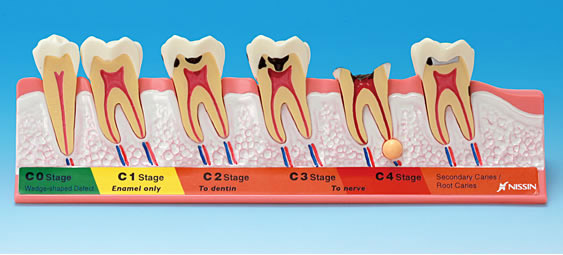
Stage One: White Spots
- The first stage of tooth decay involves the appearance of yellowish spots or chalky white areas on the surface of tooth due to the loss of calcium.
- Such tooth decay is still reversible, with proper treatment.
- The decaying tooth can be saved by the application of fluoride and certain minerals present in the saliva. During the initial stages of tooth decay, the condition can be easily countered.
Stage Two: Enamel Decay

- During this stage, the tooth enamel starts breaking below the surface layer, with the surface intact.
- If the decay persists, the surface of the tooth will be broken and this damage is irreversible.
- At this stage, your tooth needs to be cleaned and filled by your dentist.
Stage Three: Dentin Decay
- In the third stage, the decay progresses beyond the enamel into the dentin.
- At this juncture, your dentist can still restore the affected tooth with a filling.
- Pain, Sensitive to hot, cold or sweet!
- Any dental pain should be immediately noted so that the problem can be dealt with soon.
Stage Four: Involvement Of The Pulp
- The pulp of the tooth gets involved and infected due to the action of bacteria.
- Pus formation results, causing the blood vessels and nerves in the pulp to die.
- May be pain or no pain (pulp death)
- At this stage, root canal therapy is the only option of treatment.
Stage Five: Abscess Formation
- The infection reaches the root tip of the tooth.
- The bones surrounding the tooth also get infected, causing severe pain, esp. on biting!
- In serious case: You may have visible swelling on the gums, cheeks, along the affected side.
- Your dentist will prescribe antibiotics and painkiller, follow root canal therapy or remove the infected tooth at this stage.
An extremely simple fact to remember is that you can easily prevent tooth decay. The stages of tooth decay are easy note – all you need to do is pay attention to your dental hygiene and get regular check-ups done.
It is also important to spot the symptoms early, because the damage caused during the later stages of tooth decay can be irreversible.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
你知道你的牙齿构造是怎样的吗?
我们的牙齿是最身体上坚硬的物质。除了用来吃东西,它在语言沟通,及社交方面也有着重要的角色。我们的牙齿结构包括:

- 珐琅(Enamel):牙齿白色的外层部分。它是牙齿部分中最坚硬的。它主要是由磷酸钙,一个坚硬的矿物组成。
- 牙本质(Dentine):在珐琅底下,由活细胞组成,它能分泌硬矿物质。
- 牙髓 (Pulp):牙齿最软的内部结构。牙髓里头有血管和神经系统。
- 牙骨质(Cementum) : 一个牙齿根部的外围组织,使牙齿的根部牢牢地结合到牙龈和颚骨。
- 牙周膜 (Periodontal Ligament):有助于让牙齿紧紧握住下颌组织。
蛀牙如何形成?
我们的牙齿是沐浴在几乎呈中性PH值的唾液中。当牙齿周围出现酸性的环境,牙齿会被侵蚀 (脱矿)demineralization。牙齿脱矿是指牙齿在酸性的环境中,牙齿中的矿物质 (如钙)被侵蚀出来。
牙菌斑 (plaque) 是在牙齿表面上呈白色及有粘性的表层。如果没有正确的刷牙,牙菌斑可以变得更厚。牙菌斑是细菌们伟大的“家”保护它们不被唾液流冲走。如果你无法摧毁他们的“家”,他们将开始在您的牙齿上打造“大罗马文明” 。

细菌就像人类一样,它们需要进食,并消耗食物然后产生排泄物。它们排泄物是非常酸性的(它们的pH为4或更低) ,并导致牙齿被侵蚀及脱矿。
我们的唾液功能
我们的唾液是我们口中的“兵将”,帮助中和由细菌产生的酸性溶液。唾液中含有的矿物质,将有助于重新矿化
(re-mineralized)刚被轻微侵蚀的牙齿表层。但是,如果脱矿过程的继续恶化,唾液的保护功能将失效,然后牙齿将出现蛀牙/龋齿。
请记住,你和你的口腔细菌都共享相同的菜单。
请记住,你吃的东西将提供给居住在嘴里的细菌相同的食品。所以,当你吃了含有糖的食物,他们便得到了温饱的一顿饭了。并在几分钟内,他们开始生产能造成蛀牙的酸性质排泄物。所以从你要现在开始正确地刷牙。
蛀牙的阶段是什么?
有蛀牙的五个关键阶段,而这些特征是展出的蛀牙症状:

第一阶段:白点
- 蛀牙的第一阶段涉及牙齿的表面上黄色斑点或垩白色区域因钙流失的外观。
- 轻微侵蚀的牙齿可以通过氟(fluoride)和存在于唾液中的某些矿物质恢复的健康牙齿结构。
第二阶段:珐琅层蛀牙
- 在这个阶段,牙齿的珐琅质表面层下面开始被侵蚀。如果情况不被发现,牙的表面层将变得脆弱,容易造成牙齿表面层的破碎, 然后牙齿会发现有洞。
- 在这个阶段,你的牙齿需要你的牙医师清理和补牙。
第三阶段:牙本质蛀牙
- 在第三阶段中,牙齿被侵蚀的情况已超越了珐琅牙本质。
- 这个阶段,你的牙医仍然可以恢复受影响的牙齿。
- 感到疼痛,对热,冷或甜感到敏感!
- 任何牙齿疼痛,应立即寻求牙医治疗,以避免情况恶化。
第四阶段:牙髓蛀牙
- 被侵蚀的牙齿已经到了牙髓。
- 导致牙髓里的血管和神经坏死,可能会形成脓液,
- 可能是疼痛或不痛(牙髓坏死)
- 在这个阶段,根管治疗 (抽牙根)是唯一的治疗选择。
第五阶段:造成脓肿
- 感染到达牙的根尖。
- 周围牙齿的骨头也被感染,引起剧烈的疼痛,尤其在咬东西的时候!
- 严重的情况下:你的牙龈,脸颊会出现明显红肿。
- 你的牙医会给抗生素和止痛药的处方,然后开始根管治疗 (抽牙根)或者拔掉受感染的牙齿。
请记得你可以很容易地防止蛀牙。蛀牙的阶段,很容易记 - 所有你需要做的就是要注意你的口腔卫生,并得到定期牙齿检查。如果能发现症状,那么治疗会比较简单。因为蛀牙的后期阶段所造成的损害,会使治疗变得更加难及复杂。